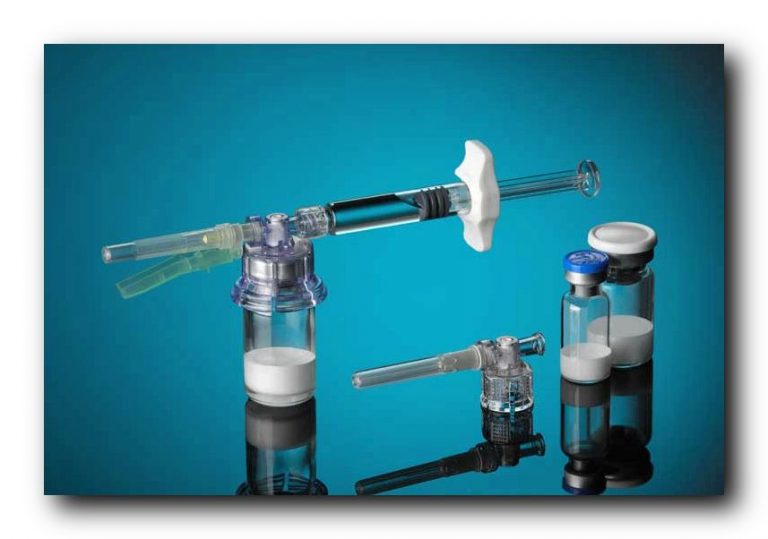
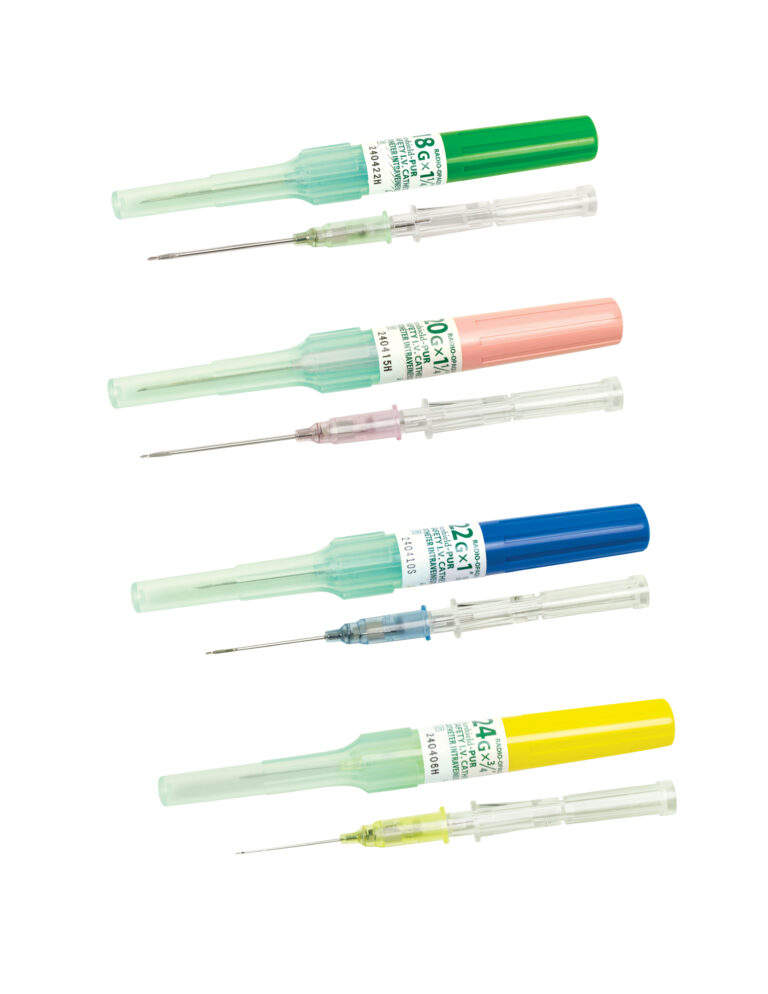
Surshield-PUR Safety I.V. Catheter
Surshiel-PUR Safety IV Catheters have a passive safety activation with SurFlash™, our exclusive catheter placement indicator. Thanks to their polyurethane construction, these safety catheters are extremely flexible, kink-resistant and durable.
For more information about Surshield-PUR Safety IV Catheters, contact Terumo Medical at 1.800.888.3786 or tmpsupport@terumomedical.com or their website.




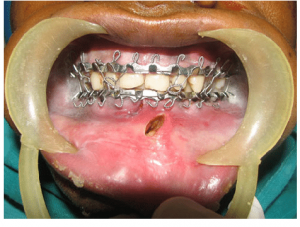 ng percutaneous injuries. The HIV or Hepatitis status of patients is rarely known. This sets up an unacceptable risk for the clinician. Newer methods of intermaxillary fixation can minimize these risks.
ng percutaneous injuries. The HIV or Hepatitis status of patients is rarely known. This sets up an unacceptable risk for the clinician. Newer methods of intermaxillary fixation can minimize these risks.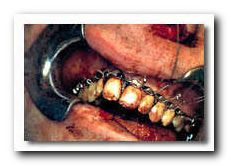

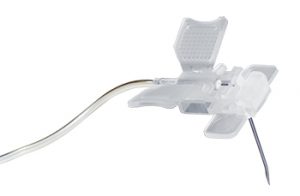

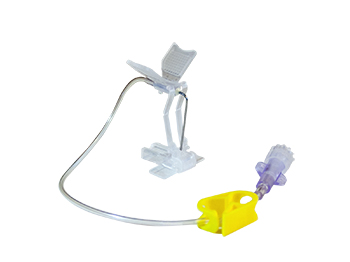
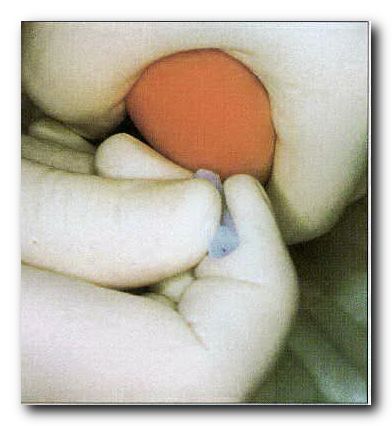



 the device is ready for use.
the device is ready for use.